Research Background
The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government is committed to the development of a knowledge-based economy, and innovation and technology are emerging industries with advantages. The establishment of the Bureau of Innovation and Technology and the Hong Kong Academy of Sciences, as well as the planning of the Hong Kong-Shenzhen Innovation and Technology Park in the Loop, signified the government’s determination to the innovation and technology industry. The government spares no effort in investing in the industry and the research community. In terms of funding, the SAR government invested more than 18 billion yuan in 2016 to promote innovation and technology through subsidies and funds. In terms of land planning, the government adjusted the industrial village policy, repossessed factory buildings that have been out of service, and used the remaining land in the industrial village for innovation and technology industries.
However, economic development cannot be separated from the supply of talents. Public education is the key to talent training. To cope with the future knowledge-based economy and innovative technology industries, the promotion of STEM education is of utmost importance to Hong Kong.
The Education Bureau published the report “Promoting STEM Education-Realizing Creative Potential” in December 2016, putting forward preliminary recommendations for promoting STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) education in primary and secondary schools. The 2015 Policy Address proposed STEM education for the first time, and the 2016 Policy Address further affirmed its support for STEM education. STEM education aims to promote students to become lifelong learners of science, technology and mathematics, so that they can meet the challenges of the 21st century, and at the same time help cultivate diverse talents in STEM-related fields to promote the development of Hong Kong.
The concept of STEM was first proposed in the United States and represents courses in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics. The promotion of STEM education is in line with the educational trend brought about by the global knowledge-based economy, slowly expanding from the United States to Europe and Asia.
Looking at STEM policy documents in Europe, America, Singapore, etc., this course is designed around the world with pragmatist rationale, hoping to train talents for the future economic needs of the region. However, compared with other STEM regions, Hong Kong’s economic structure is narrow and the secondary industry is shrinking. In addition, Chinese education has always focused on curriculum subjects and subdivided jobs, and students and parents also value educational feedback. The experience and design of overseas courses may not be fully compatible with Hong Kong. This study hopes to localize STEM education and promote an appropriate STEM education model.
The first step of localization, from STEM to STEM+ courses
The original intention of developing STEM education in Europe and the United States is to not only prepare talents for the innovative technology industry, but also hope that STEM education will solve the problem of overall students’ backwardness in mathematics and science. According to the report of the Program for International Assessment of Student Abilities (PISA), students from Eastern countries generally have higher scores in mathematics and physics than Western countries. Hong Kong’s mathematics and science scores are even among the best in PISA. Therefore, we should position STEM as the pursuit of excellence, application and development of innovative technology. This goal cannot be achieved by the efforts of individual subjects.
In 2015, PISA also showed that compared with other regions, Hong Kong students are not very interested in mathematics and science, and their ideals for entry into related industries are also low. Therefore, our expectation for STEM education is not the improvement of performance, but the improvement of attitude and interest. This goal cannot be achieved through textbooks and one-way teaching.
Hong Kong’s industrial structure is narrow, and the innovation and technology industry is still in its infancy. In other regions where STEM education is implemented, there is a large demand for talents from industries and technology companies. Parents generally have a certain understanding of STEM-related industries and outlets. However, Hong Kong lacks the advantages in this area. Therefore, the STEM environment required by graduates depends on the commonality of business and education. Build.
STEM education needs to be improved locally in Hong Kong. Our policy recommendations for STEM+ education are as follows:

Suggestion 1: Create a “STEM+ Promotion Center”
Hong Kong should refer to the practices of other countries in developing STEM education. The Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) in the United States established a committee to coordinate work related to STEM; the United Kingdom established an educational charity to support STEM network connections and consulting work; Singapore established STEM INC to independently handle the implementation of STEM. For STEM education in Shanghai, the Shanghai Stemmer International Science Education and Research Center has also been set up to deploy and integrate resources.
Since the government launched STEM education and consultation in 2015, there have been enthusiastic discussions about the slow development of STEM in the private sector. Compared with other developed countries or cities, the Hong Kong Education Bureau has indeed started late in implementing STEM education. The United States signed a related bill on STEM education in 2009 to allocate sufficient resources for long-term education development. Singapore also set the tone for supporting the future development of STEM in 2013.
In fact, Hong Kong, whether it is academia or business, already has certain resources, experience and technology to develop STEM. Driven by e-learning in the early years, the academic community has ample understanding of IT teaching, and schools have set up education centers to uniformly allocate resources. According to the research and analysis of the Chinese University of Hong Kong, the current school’s mathematics and science teachers’ teacher-directed science instruction, adaptive instruction, inquiry-based science teaching and learning practices and feedback to students (Perceived feedback) and other four teaching strategies are all higher than the OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) average, reflecting that teachers are not inferior in teaching strategies and execution capabilities. The academic community is well prepared to promote STEM education.
Hong Kong already has excellent conditions in the private and business sectors, so there is no need to re-plan STEM education from top to bottom. On the contrary, we suggest that the Education Bureau set up a “STEM+ Promotion Center” to be responsible for the parts that private organizations cannot participate in, including teacher training, and also responsible for coordinating resources between schools and business communities, so that they can play a positive role in schools. With “STEM+” as the theme, it not only promotes courses, but also links school-based training, college teacher training, business support, and foreign experience exchanges.
Main tasks of “STEM+ Promotion Center”
The Education Bureau has always established promotion centers for individual learning areas, such as the National Education Center and the IT Education Center of Excellence. The main work of “STEM+ Promotion Center” is to
conduct research on STEM education and the development of teaching materials;
- Provide on-campus support services to other schools to support the teaching methods, technology and management of STEM education;
- Research and evaluate the curriculum and teaching and learning of STEM education;
- Plan and organize professional development courses, share and promote effective educational experiences gained through practice, and organize regional or Hong Kong teacher learning communities;
- Organize cross-regional teacher exchanges and conferences in Hong Kong and other places;
- Promote Business-University-School collaboration and integrate resources from communities, non-governmental organizations, and public institutions;
- Assist in disseminating relevant government policies and measures to principals, students, parents and other stakeholders.
Recommendation 2: STEM+ phased teaching strategy
We agree with the Education Bureau’s “Promoting STEM Education-Exploiting Creative Potentials” report stated that Hong Kong’s STEM education should aim to “enhance students’ interest in learning and help them to further their studies and employment in related fields” as the goal, and conduct education that uses both hands and brains. Activities to cultivate students’ interest and curiosity.
In interviews with us, many principals and education experts said that because of the pressure of the diploma exam, it is difficult for students to continue scientific and technological research or related activities in high school. Public examinations and university promotion conditions limit the school’s attempts in STEM education. We suggest that the education sector should encourage elementary and junior high school students to participate, and increase their interest in learning before the pressure of public examinations.
STEM+ is not only a curriculum expansion, but also an extension of teaching strategies. At different stages of learning, schools should cooperate with different teaching strategies to match the level of students in the local curriculum.
- The “STEM + Play” in the early childhood and elementary school stages focuses on learning STEM in the form of activities and games, so that students have a preliminary understanding and cognition of STEM in the early childhood and elementary school stages, and increase their acceptance and interest in STEM.
- “STEM+ Inquiry-based learning” (STEM+ Inquiry-based learning) from high elementary school to junior high school , that is, adding course units in the form of project study and report. Students use curriculum knowledge in the study process, while developing their communication, creativity and problem-solving abilities, and cultivating scientific literacy.
- “STEM+ Career & Life Planning” at the high school stage is aimed at students’ pragmatic thinking. STEM can consider cooperating with the business community for career planning at the high school stage, so that parents and students can understand the way out of STEM and employment opportunities , And the challenges posed by knowledge-based economic reforms.
STEM+ as an important part of the student literacy framework
Curriculum is the rationalization of knowledge (Legalization of Knowledge). The society writes the expectations of students in general into the core curriculum, and incorporates the expectations of students who are capable and interested in learning into elective courses or extended learning activities in the classroom. As far as the promotion of STEM education is concerned, the discussion of STEM education in the society has been directed at some of the top mathematics and sciences at one time, and at the same time it generally refers to all students.
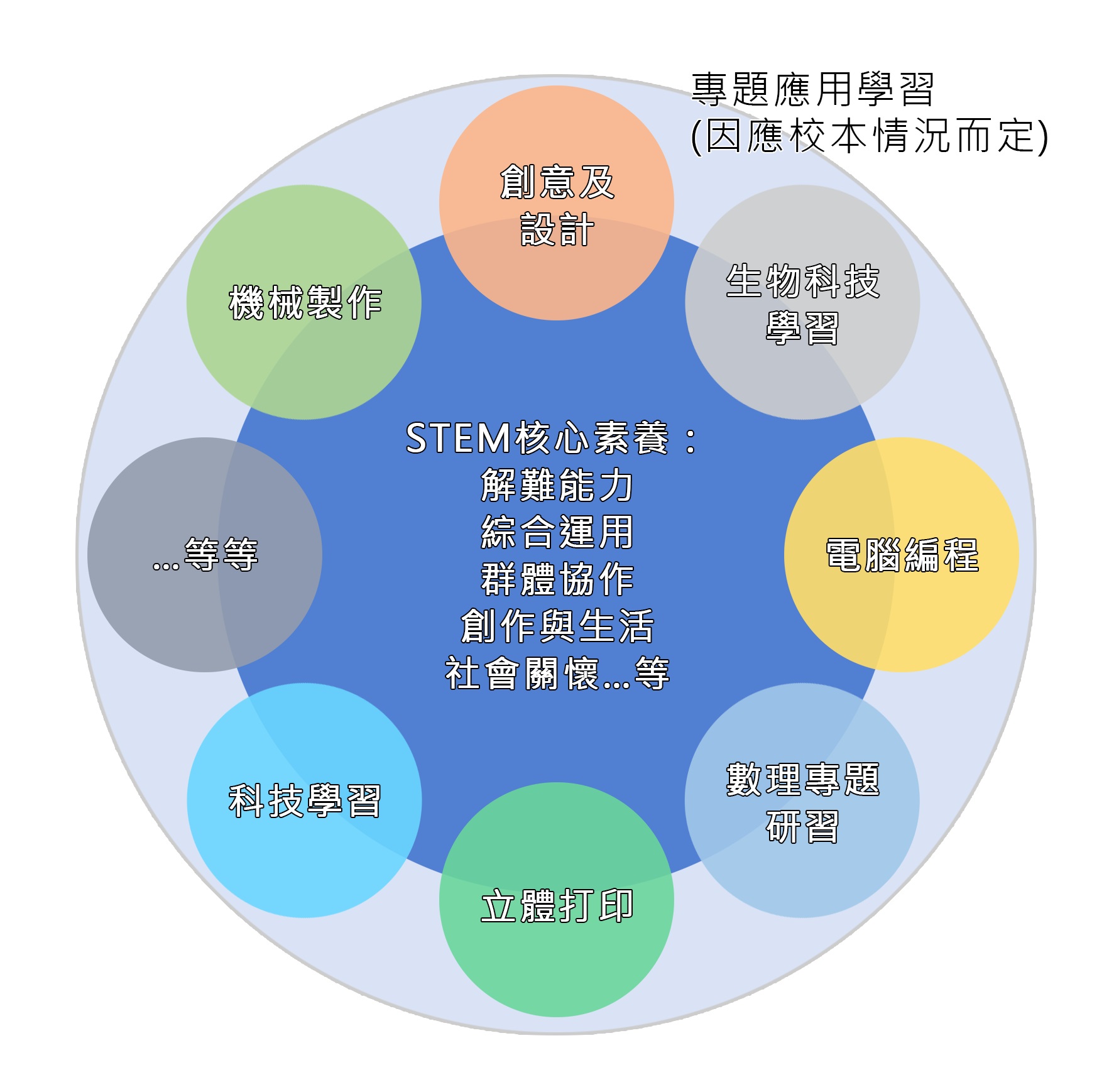
In 2015, the Hong Kong Curriculum Development Council published the first STEM policy document “Promoting STEM Education-Exploiting Creative Potential”, which has a direction for STEM learning, but there is no unified literacy framework. The Education Bureau has earlier selected four professional development schools, including Aberdeen Industrial School, Sik Sik Yuen Sik Yuen High School and Ho Yu Primary School, Lok Sin Tong Yu Jinqing Middle School, and Maryknoll Fathers’ School as a model. From their experience, it can be seen that schools will focus on individual elements in different schools in response to individual circumstances such as resources, teachers, and teachers’ interests when experimenting with STEM, such as focusing on biological exploration, mathematics and science projects, or computer programming.
In the face of global economic reforms and challenges, STEM education should have a universal part, and according to the different abilities of students and the differences in resources of the school, there should also be a part of school-based expertise. Therefore, when promoting STEM education, it is necessary to specify “STEM core literacy”. “STEM core literacy” should be required for all schools and students, and conform to the 21st century literacy of the global initiative, so that students can have future economic needs after graduation. In addition, schools can design “thematic applied learning” based on their school-based advantages, allowing students to develop their individual expertise.
STEM core literacy

At present, the development of STEM education in primary schools focuses on the curriculum update of mathematics and general studies, and strengthens the learning and teaching of different topics such as “data processing” and “probability”, so as to strengthen students’ STEM development in the form of project study and problem-based. STEM education in junior high schools advocates limiting the minimum class hours to ensure the proportion of students learning different subjects. We believe that to develop STEM exactly, we should first construct the core literacy framework of STEM so that schools and teachers can rely on it, and then adjust it flexibly according to school conditions. With reference to the experience of international development of STEM education, we should focus on STEM non-cognitive literacy and regard the study process as an indicator.
Recommendation 3: Establish a STEM+ literacy framework
Based on the experience of the United States and China in the development of STEM education, Hong Kong should establish comprehensive literacy and subject literacy at the same time. The two STEM-related curriculum files published in the United States in recent years are the 2011 K-12 Science Education Framework and the 2013 New Generation Science Education Standards, which put forward the comprehensive qualities that students should have. China has also compiled relevant scientific literacy in the Shanghai trial.
Compared with other regions, Hong Kong has rich private resources, good science and mathematics capabilities, but underdeveloped industrial industries. We refer to the STEM literacy frameworks of various regions and make adjustments to meet local conditions. We suggest that Hong Kong’s STEM + education should have the following literacy:
(a) Science and technology literacy
It refers to the content of knowledge, such as scientific principles and technological knowledge, but also to develop students’ practical ability, including scientific questioning, clearly defining problems, designing and executing project research, analyzing and interpreting data, using tools, conducting academic argumentation, and Share findings and comment.
(b) Comprehensive application and innovation literacy
The division of subjects is artificial. When students face realistic problems, there are no simple physics problems, biology problems, etc. Students should be able to exchange knowledge in the STEM category for the application of interdisciplinary comprehensive abilities. With the rapid development of science and technology, students should have innovative and learning thinking to prepare for solving problems when traditional methods fail.
(c) Problem-solving literacy
For example, how to separate difficult problems and how to recognize the connection between difficult problems and scientific knowledge. Scientific research emphasizes the use of technology to solve problems for mankind. STEM education should not be overly inclined to the absorption of knowledge by students. It should also train students’ problem-solving abilities to enhance students’ competitiveness and avoid being eliminated by social development.
(d) Group collaboration literacy
In the actual innovation and technology work environment, you need to collaborate with multiple departments and teams. It is not like a test paper for one person and individual assessment. STEM education should provide opportunities for students to help and inspire each other in group collaboration, and to construct group knowledge. Teachers can use real-world situations to ask questions. Because it is inseparable from the cooperation with other people in the real environment.
(e) Social care
The application and innovation of STEM depend on students’ concern for society. Through the processes of observation, problem-solving, and innovation, technology promotes the progress of human society, overcomes social challenges, and allows technology to positively build society. Life-related problems can also stimulate learners’ internal learning motivation, and when solving problems, they can also bring students a sense of accomplishment.
Promote business-school cooperation
The government regards schools and school-based curricula as important channels for STEM education. However, from the experience of the four professional development schools, it can be seen that the development of STEM requires more cooperation and support from outside institutions and from all sectors of society. At present, the development of STEM education is still limited to school curriculum arrangement, project study, interest groups and exhibitions and competitions between schools.
To let students understand the value and prospects of STEM, it is necessary to cooperate with the colleges and the business community, so that students can absorb first-hand information and strengthen their interest in learning; teachers can also grow from academic research, feedback and training, and schools can have enough Social network to support its development.
The business community has gradually matured in line with the development of science and technology education. Many large multinational companies have developed learning tools suitable for students, such as Apple Distinguished Educators and Hong Kong Science and Technology Park Corporation. However, these scattered but huge learning resources require an overall planning platform for centralized integration and effective use.
Recommendation 4: Create a large platform for STEM+ business schools
In addition to government funding, the government can also encourage business support. When developing STEM education in the United States, it was supported by the Gates Foundation and Carnegie Corporation of New York, allowing more than 100 corporate CEOs to create the “Equation of Change” charity organization. Through the use of funds, resources and influence, promote STEM public welfare education; encourage young people to learn STEM; promote STEM-based education reform, including considerable scholarships and employment links.
Hong Kong’s technology industry needs talents, and it needs top-down corporate connections. (1) Join companies to participate in large-scale expositions and competitions, so that the works and inventions of middle school students have the opportunity to become products and continue their creativity. (2) Provide scholarships for middle school students to study overseas or locally and carry out related research work, so as to change the existing impression of parents and middle school students on related industries. (3) Provide internships and employment commitments for middle school students with excellent research results or potential, and provide them with a stable way out.
Broaden the way out of education
After the implementation of the 2012 New Senior Secondary Curriculum, the Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education has become an important evaluation indicator for university admissions. Most university subjects admit students by calculating scores for four major subjects and two elective subjects (4+2). In response to the traditional Chinese culture of “only high school”, student selection has long been dominated by university admissions standards. According to data from the Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority, the number of students studying science subjects such as physics, chemistry, biology, integrated science and combined sciences has dropped significantly from the previous number of students studying biology, chemistry, and physics. 40% of the total dropped to 4% in 2016. At the same time, the number of students studying advanced mathematics (ie M1 or M2) dropped by 9 percentage points from 22.9% in the first HKDSE to 13.9% last year. The situation reflects that comprehensive science and advanced mathematics courses are generally excluded from the “4+2” subjects.
On the other hand, the admissions of science and engineering students in various universities in Hong Kong consider their overall abilities, including strong language proficiency and average scores in the four core subjects. Those who perform outstandingly in STEM, if they fail to meet the above requirements, will be excluded from the path to university. They will need to retake the Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education to achieve equal excellence in all subjects, or consider other pathways for further studies. We should think about the current STEM development strategy while optimizing the university entry system, providing talents with degrees and promotion opportunities, and removing academic barriers.
Recommendation 5: Improve the university admission system and recommend top students to enter relevant courses
After the educational reform, the Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education has become a single assessment, and four core subjects are used as the lowest threshold for further studies. Technological talents pursuing academic development need to take into account multiple subjects. We believe that the government should provide suitable promotion channels for outstanding students who intend to develop in innovation and technology.
We refer to the outstanding athlete recommendation program of individual colleges and universities and the sports scholarship program of the Hong Kong Institute of Sport, and suggest that the government provide funding for outstanding and intending university science, engineering and other related courses so that universities can adopt non-university joint admissions methods ( Non-JUPAS) admission. The beneficiary students only need to pass the conditional offer from the institution to meet the university’s “minimum admission requirements” to enter the university, ensuring that people can benefit from university education and develop their talents. At the same time, the admission of universities by non-university joint admissions methods will not affect their courses and university admissions results.
Funding and hardware must be aimed at improving the quality of teaching
In order to promote schools to promote STEM education-related school-based programs, the government issued a one-off grant of HK$100,000 to all primary schools in the 2015/16 school year, and provided a one-off grant of 200,000 yuan to all secondary schools in the 2016/17 school year as financial assistance . When most schools use this restricted grant, they tend to choose to purchase new types of 3D printers, metal laser cutters, and robots. On the surface, the new batch of hardware in the school helps promote the development of STEM in the school. In fact, capital and hardware-led development neglected teaching and learning software.
In the process of visiting schools, our researchers found that the experience of each school reflects that resources are not the most critical factor in the development of STEM education. First, schools can purchase different types of teaching materials according to the amount of funding. The increase in the marginal price of teaching materials does not necessarily reflect the marginal benefit of teaching quality. Second, in response to the class optimization plan in recent years, the school premises have also freed up classrooms and space for various activities and teaching purposes.
On the contrary, to specifically promote STEM literacy and cultivate students’ comprehensive ability, curriculum design and teacher team are far more important than hardware. When discussing with us, teachers and experts stated that teachers’ subject knowledge, enthusiasm for STEM, curriculum and teaching methods and other software are the keys to the success of STEM education. At present, each school provided by the government provides a lump sum funding, which makes it difficult to continuously develop curriculum content or conduct teacher training. This needs to be improved.
In addition to the purchase cost of technology products, there are also depreciation and maintenance costs. When purchasing a technology product, schools should consider the sustainability of the product for the development of STEM, whether the technology product is a temporary craze, and whether the technology product requires high maintenance costs.
Recommendation 6: Beware of turning the cart before the horse and cater to current technology too much
STEM+ education is to provide talents for the future economy. The distance between students’ exposure to STEM+ education in the school and their graduation can be more than ten years. Technology is changing with each passing day, and the technology used in school today will inevitably become the history of graduation. If the curriculum and class hours focus on the use of current technology, rather than enhancing students’ interest in learning and STEM+ core literacy, it will be a waste of the last.
The results of the Hong Kong Research Institute’s “Hong Kong Students’ I Literacy and Survey” (see Chapter 5 for details) show that Hong Kong students have a good understanding of current technology and electronic products. Good at getting in touch with new technological skills. There is no need for students to overlearn existing technology applications.
Summary: Government-private cooperation to develop innovative and technological talents
We believe that Hong Kong has the experience and foundation for the development of STEM+ education. The Education Bureau can provide policy leadership and curriculum resources, and make good use of the scattered achievements of academia, society and business. On the one hand, the government should carry out education coordination from top to bottom. On the other hand, it should reserve a certain amount of space. Through the semi-official “STEM+ Promotion Center”, the private sector can use creativity to experiment with different teaching strategies and teaching plans, and mobilize business schools. In addition to cooperation, promote cooperation with educational and voluntary groups and institutions, and conduct parent education and teacher training at the same time. In terms of further studies, the government should also formulate plans with tertiary institutions to attract talented students into undergraduate courses related to STEM.
Finally, in addition to curriculum, teaching and learning, and further studies, the success of STEM+ education in Hong Kong is also a key factor in the employment of students. The education sector in Hong Kong hopes that the government can promote the diversification of Hong Kong’s industries and implement the three-creation economy of creativity, innovation and entrepreneurship, so that STEM+ students can stay in Hong Kong for development and contribute to society.

Convener Mr. Zeng Yucheng (second from right), Executive and Research Director Mr. Feng Keqiang (first from right), honorary researcher President Dai Xili (second from left) and researcher Mr. Feng Zhizheng (first from left) published research reports on STEM topics.





